# Intro
- We use tabs and not spaces for indentation
- We prefix private class variables with an underscore
- We prefix private methods with an underscore
- We use camelCase for variables, not snake_case:
self._myVariableName
- We use UPPER_CASE for class static vars or final vars:
LIGHT_SPEED = 299792458
- We use PascalCase for class names
- We use 2 empty lines around met is ods
- We do strong type method variables
- We do strong type method returns:
- Return '-> None' is not mandatory
- We speak English
- We use properties getters and setters, not getters and setters
- We really care for anti-patterns: https://docs.quantifiedcode.com/python-anti-patterns/
- We use fstrings and dropped the usage of .format() when possible:
print(f'Hi! my name is {name}')instead ofprint('My name is {}'.format(name)
- Python 2 is dead
- Init dictionaries and lists with
dict()andlist()and not with{}or[] - Do never shadow a builtin var or method
- We don't copyright the files themselves. We believe in sharing, and the main file contains authors. The project is licensed under GPLv3.
# Pycharm settings
To make things easier, I have shared my pycharm settings under a GitHub repository. Simply open pycharm, click File in the top left corner and choose Settings repository and choose Overwrite local
NOTE: You may have to also CTRL+ALT+s to open the settings' editor manually. Then go to the menu Version control >> GitHub and if you had a previous GitHub account stored in here then it may get overwritten with ours. If so click that name then remove it by clicking the " - " then click the " + " and re add your GitHub account.
# Reformat your code
Pycharm comes with a powerful inbuilt code formatter which you can use to adapt your code to our guidelines once you have linked your pycharm to our settings repository. Right-click on your project and choose Reformat code. You'll be presented with a popup to choose some options:
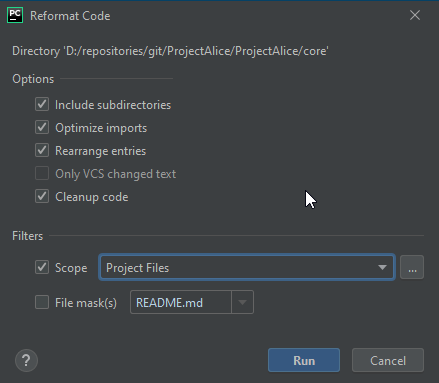
If you don't see that reformat option on a right click then it can also be found under the menu heading code on the toolbar.
# Check your code
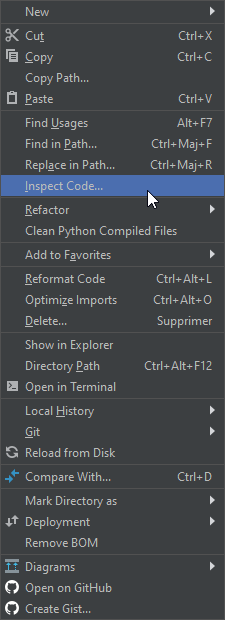
Pycharm comes with an inbuilt code checker. Beside the "per file" instant check (top right corner, green tick if ok) you can run an analysis on your code by right-clicking your project and choose Inspect code:
# Automatic code check
Pycharm has a Sonarcloud plugin that can check your code to make sure it is following our guidelines!
- Create an account on SonarCloud
- Contact us to add you as a skill dev, in order for you to generate your access token
- Once you've been added in our skill dev group, go to your SonarCloud profile, under security, and generate a new access token.
- In Pycharm open your settings
- Go to
Plugins - Search and install
SonarLint
- Under
ToolsselectSonarLintand click on the+to add a new connection
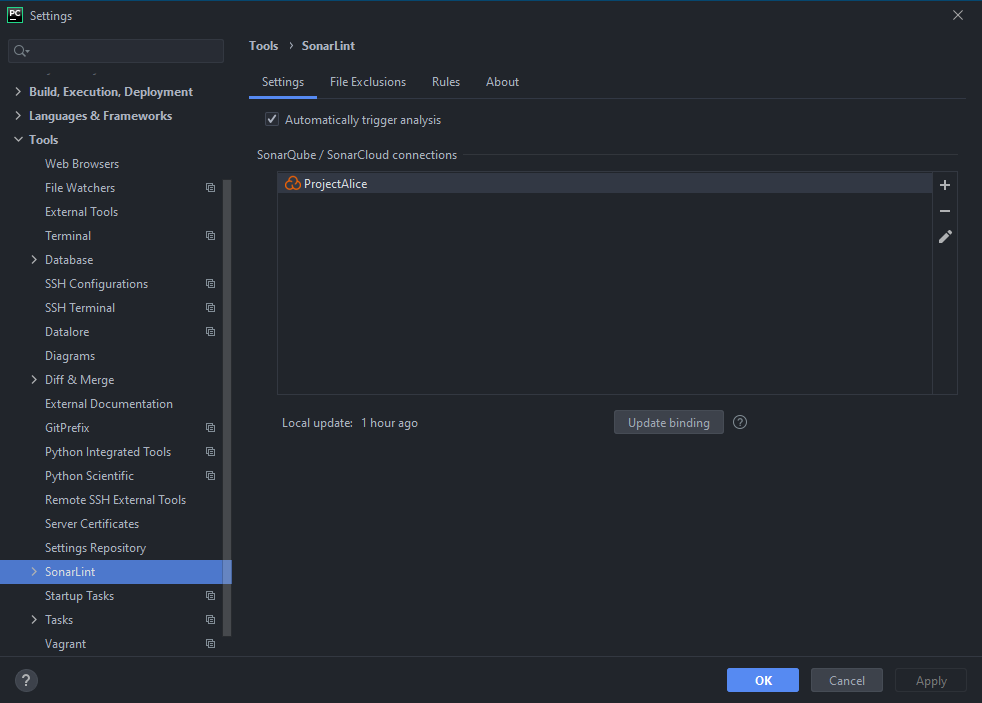
- Name it
ProjectAliceand chooseSonarCloud, then click on next
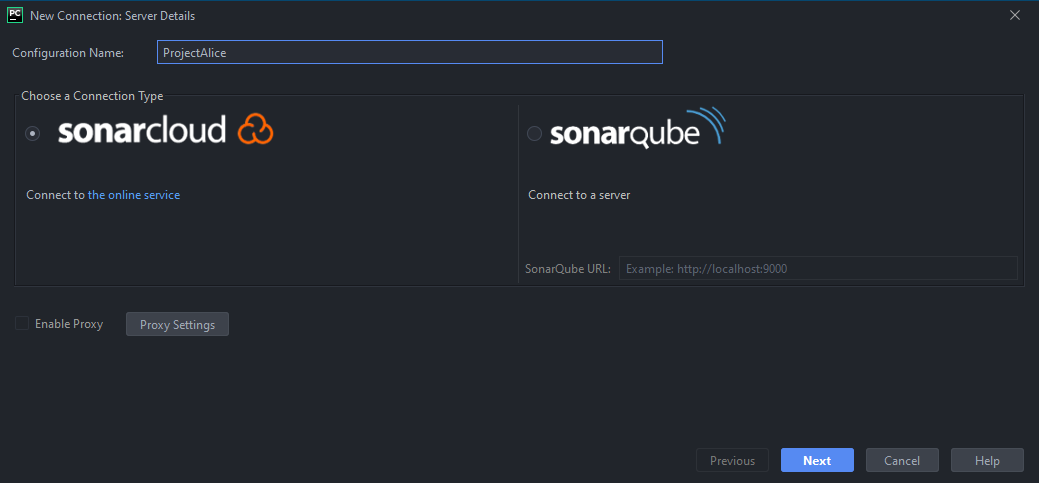
- Enter your SonarCloud token, and you are good to go!